Report: NASA’s aqua satellite helps confirm subtropical storm alpha
Subtropical Storm Alpha has formed near the coast of Portugal, becoming the first named storm using the Greek Alphabet list, now that the annual list of names is exhausted. NASA's Aqua satellite obtained visible...
Study: Defying a 150-year-old rule for phase behavior
Frozen water can take on up to three forms at the same time when it melts: liquid, ice and gas. This principle, which states that many substances can occur in up to three phases...
Scientists discover a novel family of toxins used in bacterial competition
Researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil have characterized a novel family of anti-bacterial toxins present in bacteria, including Salmonella enterica. This species uses toxic proteins to kill other bacteria in...
Study: Shift in West African wildmeat trade suggests erosion of cultural taboos
New research by the University of Kent's Durrell Institute of Conservation and Ecology (DICE) has demonstrated a clear fluctuation in the trade of wildmeat in and around the High Niger National Park in Guinea,...
Researchers identify gene family key to unlocking vertebrate evolution
New University of Colorado Boulder-led research finds that the traits that make vertebrates distinct from invertebrates were made possible by the emergence of a new set of genes 500 million years ago, documenting an...
Research estimates nearly 90,000 cancer cases diagnosed in adolescents and young adults
A new report examining cancer in adolescents and young adults (AYAs), defined as diagnoses occurring during ages 15 to 39, provides updated estimates of the contemporary cancer burden in this age group, predicting that...
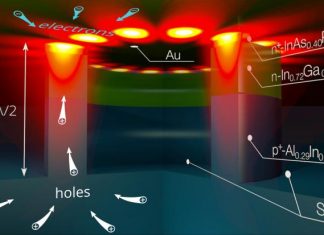
Scientists make electrical nanolasers even smaller
Researchers from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology and King's College London cleared the obstacle that had prevented the creation of electrically driven nanolasers for integrated circuits. The approach, reported in a recent...
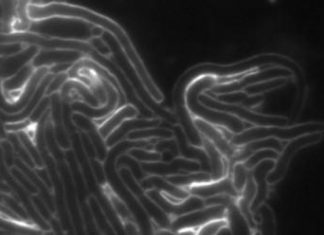
Study: Human white blood cells use molecular paddles to swim
Human white blood cells, known as leukocytes, swim using a newly described mechanism called molecular paddling, researchers report in the September 15th issue of Biophysical Journal. This microswimming mechanism could explain how both immune...
Study: Ocean algae get ‘coup de grace’ from viruses
Scientists have long believed that ocean viruses always quickly kill algae, but Rutgers-led research shows they live in harmony with algae and viruses provide a "coup de grace" only when blooms of algae are...
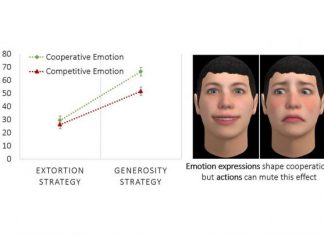
Study: Future autonomous machines may build trust through emotion
Army research has extended the state-of-the-art in autonomy by providing a more complete picture of how actions and nonverbal signals contribute to promoting cooperation. Researchers suggested guidelines for designing autonomous machines such as robots,...