Study: Warming ocean, old-forest loss put a squeeze on an elusive seabird
Squeezed by changing ocean conditions that limit their food options and the long-term loss of old forest needed for nesting, marbled murrelets would benefit most from conservation efforts that take both ocean and forest...
Study: Cities beat suburbs at inspiring cutting-edge innovations
The disruptive inventions that make people go "Wow!" tend to come from research in the heart of cities and not in the suburbs, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that, within metro areas, the majority...
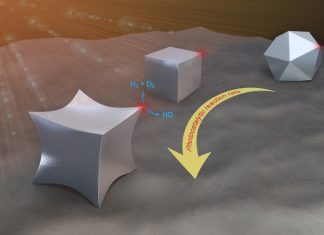
Study: Shape matters for light-activated nanocatalysts
Points matter when designing nanoparticles that drive important chemical reactions using the power of light.
Researchers at Rice University's Laboratory for Nanophotonics (LANP) have long known that a nanoparticle's shape affects how it interacts with...
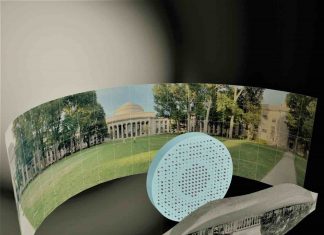
Researchers produce a fisheye lens that’s completely flat
To capture panoramic views in a single shot, photographers typically use fisheye lenses -- ultra-wide-angle lenses made from multiple pieces of curved glass, which distort incoming light to produce wide, bubble-like images. Their spherical,...
Research shows vitamin E needed for proper nervous system development
In research with key ramifications for women of childbearing age, findings by Oregon State University scientists show that embryos produced by vitamin E-deficient zebrafish have malformed brains and nervous systems.
"This is totally amazing -...
Study: Colorado’s famous aspens expected to decline due to climate change
Along three scenic drives through Colorado's Rocky Mountains in fall, tourists will see less of a brilliant golden tree in the next 100 years, researchers from North Carolina State University projected in a new...
Study: Choosing the right cover crop to protect the soil
Farmers around the world are keen to protect their most important asset: their soil. The soil supports and enriches their crops. But the relatively thin layer of topsoil can readily wash away into streams,...
Study: Device could help detect signs of extraterrestrial life
Although Earth is uniquely situated in the solar system to support creatures that call it home, different forms of life could have once existed, or might still exist, on other planets. But finding traces...
Study: Climate crisis ages fish, amphibians and reptiles
Climatic conditions are changing at an unprecedented rate, affecting mainly fish, amphibians and reptiles, ectothermic animals that are unable to generate their own internal heat. With heat waves and rising temperatures, these organisms experience...
Study: Undersea earthquakes shake up climate science
Despite climate change being most obvious to people as unseasonably warm winter days or melting glaciers, as much as 95 percent of the extra heat trapped on Earth by greenhouse gases is held in...