Scientists reveal the evolutionary origins of the plant that sends cats into a frenzy
Scientists have discovered how catmint gained its ability to send felines into a state of frenzy.
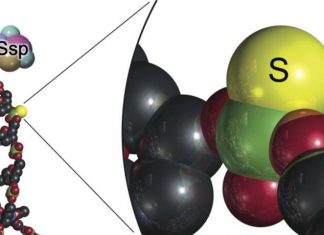
By unpicking its genetic makeup, researchers have discovered how catmint evolved to make nepetalactone, the molecule responsible for its...
Scientists uncover new anti-phage defense mechanisms
Scientists from Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT’s research enterprise in Singapore, have discovered a new anti-phage defense mechanism found in some bacteria, which use previously unknown features to protect their DNA....
Study: New evidence shows giant meteorite impacts formed parts of the moon’s crust
New research published today in the journal Nature Astronomy reveals a type of destructive event most often associated with disaster movies and dinosaur extinction may have also contributed to the formation of the Moon's...
Study: Bumble Bee Disease, Reproduction Shaped by Flowering Strip Plants
Flowering strips – pollinator-friendly rows of plants that increase foraging habitat for bees – can help offset pollinator decline but may also bring risks of higher pathogen infection rates for pollinators foraging in those...
Research Suggests a Polymer Composite Could Serve as Lighter
A new study from researchers at North Carolina State University suggests that a material consisting of a polymer compound embedded with bismuth trioxide particles holds tremendous potential for replacing conventional radiation shielding materials, such...
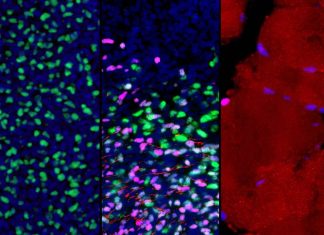
Researchers create first roadmap of human skeletal muscle development
An interdisciplinary team of researchers at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center for Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA has developed a first-of-its-kind roadmap of how human skeletal muscle develops, including the...
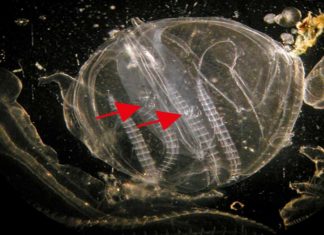
Study: Cannibalism helps invading invertebrates survive severe conditions
A new study, published in Communications Biology, shows that the prolific comb jelly, a marine invertebrate invader from North America that now frequently washes up on Baltic shores, is able to expand their geographical...
Study: Climate change could cause decline of some alpine butterfly species
The long-term effects of climate change suggests that the butterfly effect is at work on butterflies in the alpine regions of North America, according to a new study by University of Alberta scientists—and the...
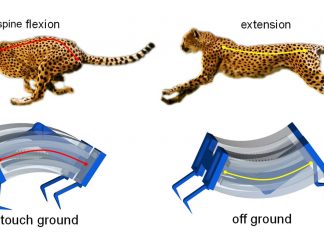
Inspired By Cheetahs, Scientists Build Fastest Soft Robots Yet
Inspired by the biomechanics of cheetahs, researchers have developed a new type of soft robot that is capable of moving more quickly on solid surfaces or in the water than previous generations of soft...
Well-being podcast making connections in time of social distancing (research)
Moving into the pandemic lockdown, Assistant Prof. Jen Watt says people are starting to realize what’s happening when young people can’t make the connections provided in school.
“Although we have always known it, Covid-19 has...