Study: Ultra-bright X-ray source awakens near a galaxy not so far away
A new ultra-bright source of X-rays has awakened in between our galactic neighbours the Magellanic Clouds, after a 26-year slumber. This is the second-closest such object known to date, with a brightness greater than...
Study: Alien frog invasion wreaks havoc on natural habitat
Indiscriminate feeding by an alien population of the carnivorous spotted-thighed frog - could severely affect the native biodiversity of southern Australia according to a new study by the University of South Australia.
The invasive amphibian...
Study: Asian tiger mosquito gains ground in Illinois
Researchers report that the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus, has become more abundant across Illinois in the past three decades. Its spread is problematic, as the mosquito can transmit diseases - like chikungunya or...
Study: Conserving biodiverse ‘slow lanes’ in a rapidly changing world
The notion of conserving climate change refugia - areas relatively buffered from current climate change that shelter valued wildlife, ecosystems, and other natural resources - is only about 10 years old, but the field...
Study: Ocean uptake of CO2 could drop as carbon emissions are cut
Volcanic eruptions and human-caused changes to the atmosphere strongly influence the rate at which the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide, says a new study. The ocean is so sensitive to changes such as declining greenhouse...
Study: How bacteria fertilize soya
Plants need nitrogen in the form of ammonium if they are to grow. In the case of a great many cultivated plants, farmers are obliged to spread this ammonium on their fields as fertiliser....
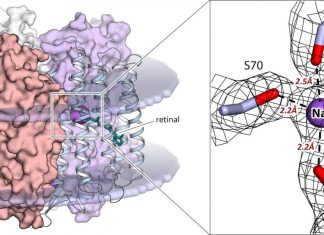
Study: Biophysicists reveal how optogenetic tool works
An international research team has for the first time obtained the structure of the light-sensitive sodium-pumping KR2 protein in its active state. The discovery provides a description of the mechanism behind the light-driven sodium...
Study: Class of stellar explosions found to be galactic producers of lithium
A team of researchers, led by astrophysicist Sumner Starrfield of Arizona State University (ASU), has combined theory with both observations and laboratory studies and determined that a class of stellar explosions, called classical novae,...
Study: A rising tide of marine disease? How parasites respond to a warming world
Warming events are increasing in magnitude and severity, threatening many ecosystems worldwide. As the global temperatures continue to climb, it also raises uncertainties as to the relationship, prevalence, and spread of parasites and disease.
A...
Research shows erosion of ozone layer responsible for mass extinction event
Researchers at the University of Southampton have shown that an extinction event 360 million years ago, that killed much of the Earth's plant and freshwater aquatic life, was caused by a brief breakdown of...