Study: Dragonflies reveal mercury pollution levels across US national parks
A citizen science program that began over a decade ago has confirmed the use of dragonflies to measure mercury pollution, according to a study in Environmental Science & Technology.
The national research effort, which grew...
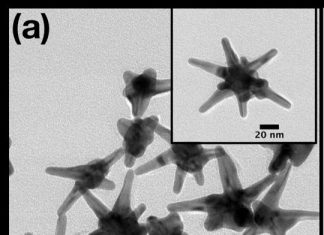
Study: Silver-plated gold nanostars detect early cancer biomarkers
Biomedical engineers at Duke University have engineered a method for simultaneously detecting the presence of multiple specific microRNAs in RNA extracted from tissue samples without the need for labeling or target amplification. The technique...
Study: River plants counter both flooding and drought to protect biodiversity
'Water plants are a nuisance in streams, blocking the flow. You should remove them'. This notion has for many years determined how streams were managed to prevent flooding during high rainfall events. Research by...
Scientists part of international effort to save critically endangered seabird
The global population of the critically endangered Chinese crested tern has more than doubled thanks to a historic, decade-long collaboration among Oregon State University researchers and scientists and conservationists in China, Taiwan and Japan.
The...
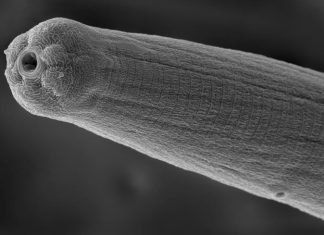
Study: Parasitic worm venom evades human immune system
It's likely that billions of people are unaware they have been infected with parasitic worms. A UC Riverside scientist has won $1.8 million to try and understand why.
The National Institutes of Health granted an...
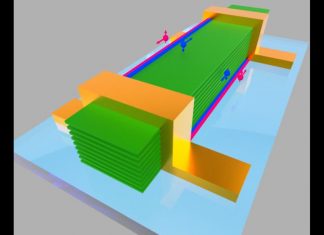
Study: Higher-order topology found in 2D crystal
Over the last decade, the field of condensed matter physics has experienced a golden age with the discovery of new materials and properties, and related technologies being developed at breakneck speed thanks to the...
Study: Antarctica more widely impacted by humans than previously thought
Antarctica is considered one of the Earth's largest, most pristine remaining wildernesses. Yet since its formal discovery 200 years ago, the continent has seen accelerating and potentially impactful human activity.
How widespread this activity is...
Study: Geoengineering is just a partial solution to fight climate change
Could we create massive sulfuric acid clouds that limit global warming and help meet the 2015 Paris international climate goals, while reducing unintended impacts?
Yes, in theory, according to a Rutgers co-authored study in the...
Study: Clear strategies needed to reduce bushmeat hunting
Extensive wildlife trade not only threatens species worldwide but can also lead to the transmission of zoonotic diseases. An international research team led by the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the German...
Study: Widely used blood test could advance heart failure treatment
Biomedical experts believe that half of heart failure patients likely have low levels of the thyroid hormone T3 in their cardiac tissue. While heart failure symptoms are commonly attributed to cardiovascular conditions like coronary...