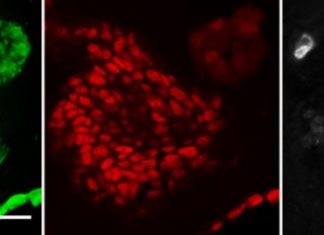
Study: A scientific advance in studying early-stage lung cancer
Lung cancer is the leading cancer killer in the U.S. It is often missed in its earlier stages, and while recent imaging advances have enabled earlier detection, there are still no targeted treatments for...
Study: Did our early ancestors boil their food in hot springs?
Some of the oldest remains of early human ancestors have been unearthed in Olduvai Gorge, a rift valley setting in northern Tanzania where anthropologists have discovered fossils of hominids that existed 1.8 million years...
Study: Dams exacerbate the consequences of climate change on river fish
A potential response of river fish to environmental changes is to colonize new habitats. But what happens when dams and weirs restrict their movement? And are native and alien species similarly affected? Researchers from...
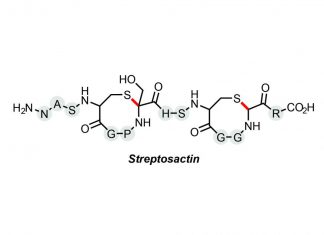
Study: Princeton lab discovers small “Cain-and-Abel” molecule
A new bacterial molecule with the unsavory tendency to track down and kill others of its own kind has been discovered in the human microbiome by researchers at Princeton's Department of Chemistry. Named Streptosactin,...
Researchers uncover a novel approach to treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute, Fondazione Santa Lucia IRCCS, and Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore in Rome have shown that pharmacological (drug) correction of the content of extracellular vesicles released within...
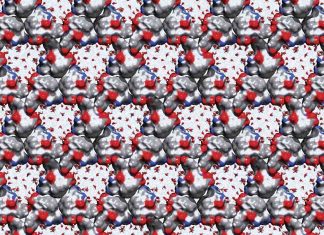
Study: CCNY engineer Xi Chen and partners create new shape-changing crystals
Imagine harnessing evaporation as a source of energy or developing next generation actuators and artificial muscles for a broad array of applications. These are the new possibilities with the creation by an international team...
Study: Heated rivalries for pollinators among arctic plants
Insect pollination is as important to Arctic plants as it is to plants further south. When flowers abound, the plants have to compete for pollinators. Researchers at the University of Helsinki reveal that higher...
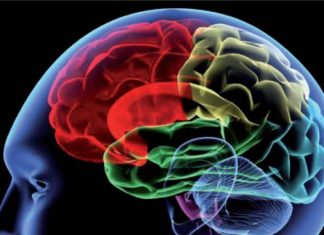
Study: TRESK regulates brain to track time using sunlight as its cue
Research from the University of Kent has found that TRESK, a calcium regulated two-pore potassium channel, regulates the brain's central circadian clock to differentiate behaviour between day and night.
It was previously understood that the...
Research examines how civil wars affect wildlife populations
A new study comprehensively reveals how civil wars impact wildlife in countries affected by conflict.
Researchers at the University of East Anglia (UEA), in the UK, Federal University of Paraíba (UFPB), Brazil, and University of...
Study: Transplanted brown-fat-like cells hold promise for obesity and diabetes
Obesity is the main cause of type 2 diabetes and related chronic illnesses that together will kill more people around the globe this year than the Covid-19 coronavirus. Scientists at Joslin Diabetes Center have...